Lost with “404 Page Not Found” errors?
These errors drive visitors away, hurt your search rankings, reduce your traffic, and damage your reputation; but worry not! We break down what 404 errors are, why they happen, and how to fix and prevent them effectively in this guide.
What is a 404 Error?
A 404 Not Found error tells us that the server couldn’t locate the requested resource. It’s the standard HTTP status code for a failed request, sent from the server back to the browser.
This error can happen for various reasons. For instance, clicking a search engine result may lead to a missing page, or a link on a website might point to an internal URL that no longer exists.
A 404 error doesn’t specify the cause. If you encounter it while browsing, it’s unclear whether the file is missing or the link’s path is incorrect.
Error 404 Not Found: Message Variations
The most common variations of the message displayed on a 404 error, depending on the browser or the custom 404 page used by a website, are:
- Error 404
- 404 Not Found
- HTTP Error 404
- Not Found
- Page Not Found
- The page cannot be found
- The requested URL was not found on this server
Common Causes of 404 Errors
404 errors can occur for various reasons, and they may not indicate a problem with your website.
1. Typos in URLs
Users may occasionally type a URL incorrectly, leading to a 404 error. This is an expected part of browsing and signifies the page doesn’t exist.
2. Broken Internal Links
A 404 error on specific pages often means the URL or permalink was changed without a proper redirect. For example, changing a permalink from “about-us” to “company” without a redirect will cause this error. Ensure redirects are set up to avoid broken links. If the issue affects all pages, update your permalink settings to resolve it.
3. Deleted or Moved Pages
When pages are deleted or moved, old URLs will trigger a 404 error. Use proper redirects to guide users to the correct location and maintain a seamless browsing experience.
4. Overlooked Broken Links
Sometimes, websites accumulate broken links over time. This is common when old pages, posts, or even images are removed without updating or redirecting the links pointing to them. Websites may still rank well in search engines, even if some of their URLs are unavailable, but fixing these issues will improve both user experience and SEO.
5. Issues with Permalinks or Server Configuration
Another cause of 404 errors is improper permalink settings or server configuration issues. You may also encounter 404 errors when clicking on external links within a website (e.g., links to other blogs or portals). External links are often not monitored or updated regularly, resulting in broken links and 404 errors.
Try our Award-Winning WordPress Hosting today!

Why Fixing 404 Errors Is Crucial
404 errors hurt trust—with both users and search engines—damaging your website’s reputation and search rankings. We don’t want that.
Frequent errors can erode user confidence in your site. Visitors may question whether the content they seek is available and leave for alternatives.
For search engines, repeated 404 errors indicate poor site maintenance. Crawlers may ineffectively index your pages, and if too many links lead to errors, your search rankings may drop—or your site may be removed from the index altogether.
This can lead to a significant decline in organic traffic.
How to Check for 404 Errors
That said, it is essential to take precautionary measures to prevent HTTP 404 pages, both internally and externally. The first step is identifying the problem.
Fortunately, there are free tools to help you find the broken links causing 404 errors on your site. Here’s how:
Google Search Console
Log in to your Google account and navigate to the Google Search Console overview page. Select the domain you want to check from the upper left.
If you haven’t already, you should add your domain as a property.
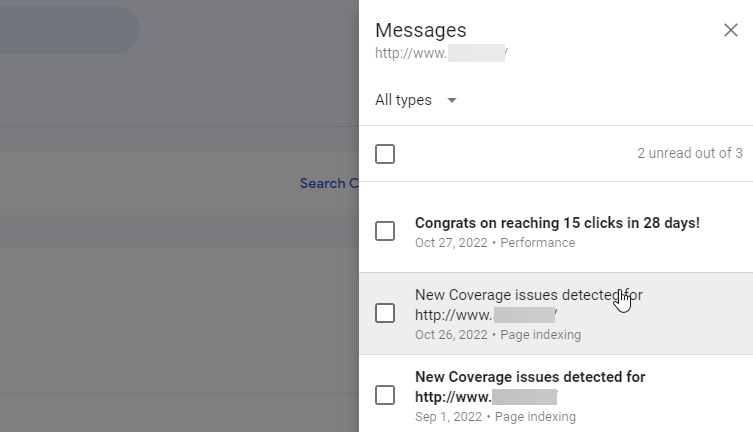
Then, click the notifications icon in the upper right to access messages.
Google Search Console will guide you through fixing 404 errors by providing a table of affected URLs.
Other popular free tools that can help you with this are Google Analytics, W3C Link Checker, Deadlinkchecker, and ATOMSEO.
Processing Access Logs from Your Provider to Detect 404 Errors
If your hosting provider offers access logs, you can analyze them to find 404 errors. These logs record all requests made to your site, including failed requests that result in 404 errors. By reviewing your site’s access logs, you can identify broken links, missing pages, and external sources linking to non-existent URLs.
Pressidium Dashboard: Error Logs
At Pressidium, we provide detailed insights into site traffic, including 404 errors, helping you quickly detect and fix broken links.
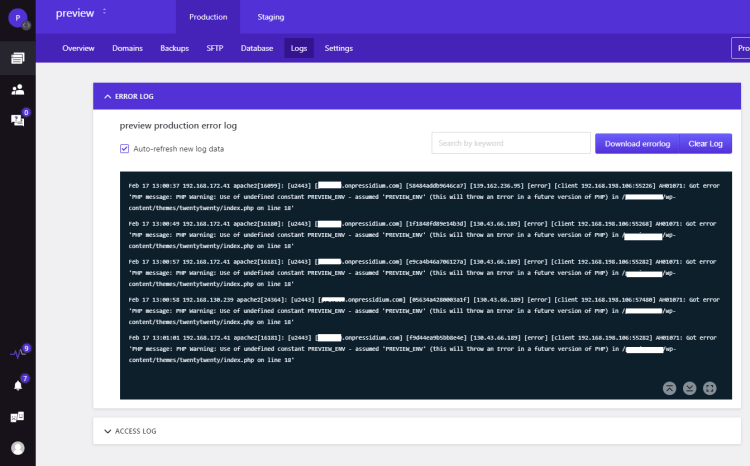
You can access these error logs directly from your dashboard and analyze them to identify URLs that return 404 errors and determine their causes. The log viewer offers features like auto-refresh, search, and the ability to download or clear logs, facilitating efficient troubleshooting.
How to Fix 404 Errors
To resolve a 404 error, start by identifying its cause. Advanced hosting providers such as Pressidium offer tools to track when visitors request unavailable pages. If these tools aren’t available, consider the following steps:
- Check for typos. Start by eliminating the most straightforward cause: typos. Before diving deeper into troubleshooting, verify that the URL is free of spelling errors or missing trailing slashes.
- Clear browser cache. If the error appears on only one device, cached data may be the culprit. Prompting visitors to clear the browser cache and cookies will resolve the issue.
Resolve 404 Errors by Using a WordPress Plugin
A WordPress Plugin can simplify the process of addressing 404 errors. Here are two highly effective options:
All 404 Redirect to Homepage

If you’re looking for a quick and simple solution, All 404 Redirect is the way to go.
This plugin redirects all non-working URLs to your homepage, saving you time on manual redirects. To get started:
- Install and activate the plugin.
- Enable it, and your basic setup is complete; set it and forget it.
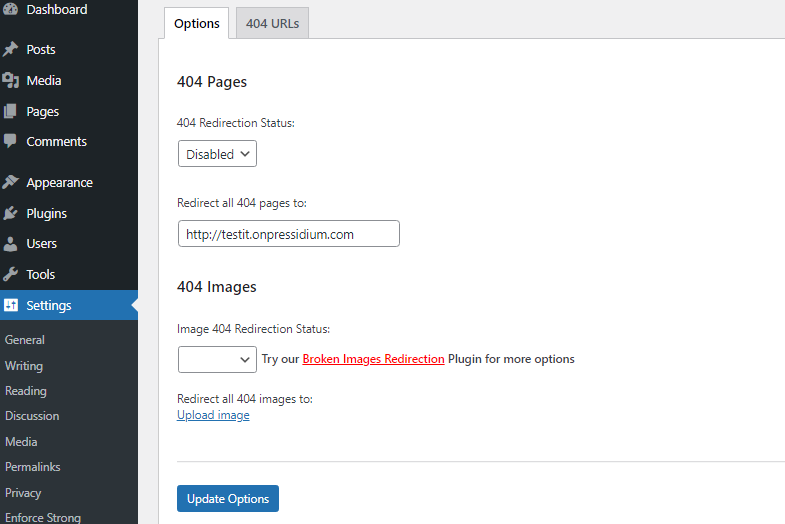
For more options, visit the plugin’s settings. You can change the default redirection URL from the homepage to any valid URL. Be cautious—invalid URLs can lead to redirect loops.
NOTE: Google discourages homepage redirection. Instead, create a custom, user-friendly 404 page to avoid “soft-404 errors,” which could impact your SEO.
Also, there is a link to the 404 Image Redirection plugin in case you want to redirect missing images to a default image, and a 404 URLs tab.
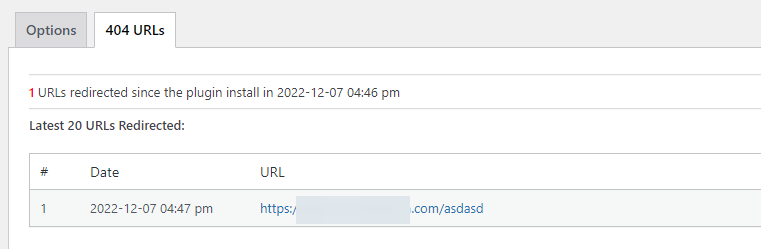
In the 404 URLs tab, you can review the redirected 404 links you have already added.
Use 301 Redirects

For URLs permanently moved to new locations, the 301 Redirects plugin is an excellent choice. This tool prevents 404 errors by redirecting visitors to the correct URL.
Here’s what you can do under Settings -> 301 Redirects:
- Create and manage redirects (301, 302, or 307).
- View logs to identify 404 triggers.
- Import and export redirect rules using CSV files.
Alternatively, consider using Quick Page/Post Redirect Plugin or SEO Redirection Plugin.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What Should I Include on a Custom 404 Page?
A custom 404 page is a user-friendly way to guide visitors when they land on a non-existent page. Here’s what to include:
- A clear message stating that the page is not found (e.g., “Oops! The page you are looking for is not available”).
- A search bar so users can easily find what they are looking for.
- Navigation links to important sections or your homepage.
- A lighthearted touch or humor (optional) to reduce frustration.
2. What’s the Difference Between 301 and 302 Redirects?
301 Redirect: This is a permanent redirect, telling search engines and users that a page has been permanently moved to a new URL. It passes most of the SEO value to the new page.
302 Redirect: This is a temporary redirect, indicating that the move is not permanent. SEO value is not passed as effectively as with a 301 redirect.
3. Should I Redirect all 404 Errors to the Homepage?
Redirecting all 404 errors to the homepage is a quick solution, but it’s not recommended for SEO. Google considers this a “soft 404,” which can negatively impact your site’s ranking. Instead, it’s better to use 301 redirects to specific relevant pages or create a custom 404 page that guides users to the correct content.
4. How do I Check for 404 Errors on my Website?
You can use tools like Google Search Console, Google Analytics, or third-party tools like W3C Link Checker to identify 404 errors. These tools scan your site and report any broken links so you can fix them before they impact your users and SEO.
5. Are 404 Errors Bad for SEO?
Yes, 404 errors can harm your SEO in the long term if not addressed. Search engines may lower your website’s ranking if it frequently serves up broken links, as it suggests poor site maintenance. However, fixing or redirecting 404 errors helps maintain a healthy site and preserves SEO value.
Conclusion
Stop 404 errors from affecting your site’s traffic and user experience. Resolving 404-related issues is crucial for maintaining a seamless browsing experience and improving your SEO performance.
Now you have a clearer understanding of what causes 404 errors and how to fix them. Read our guide on how to create a custom 404 page for your WordPress site too.
Start Your 14 Day Free Trial
Try our award winning WordPress Hosting!